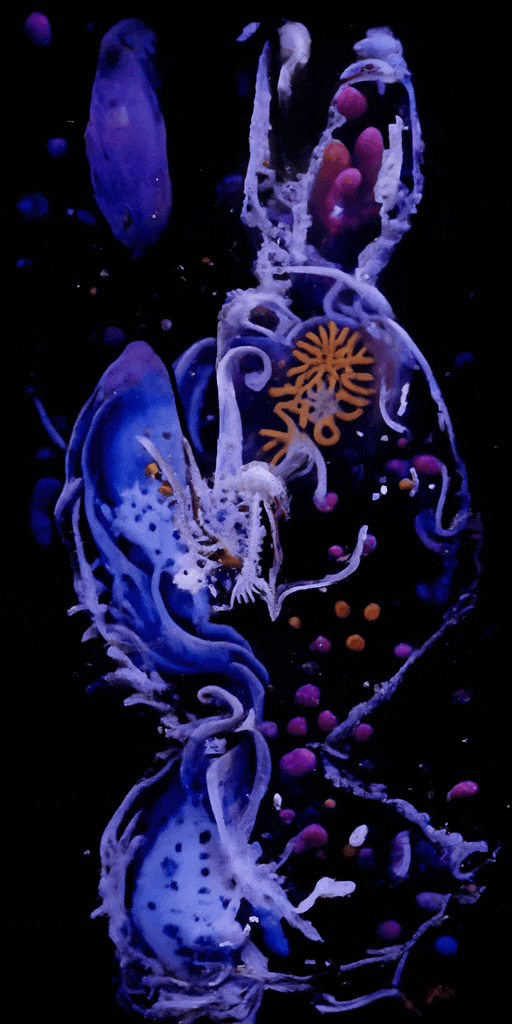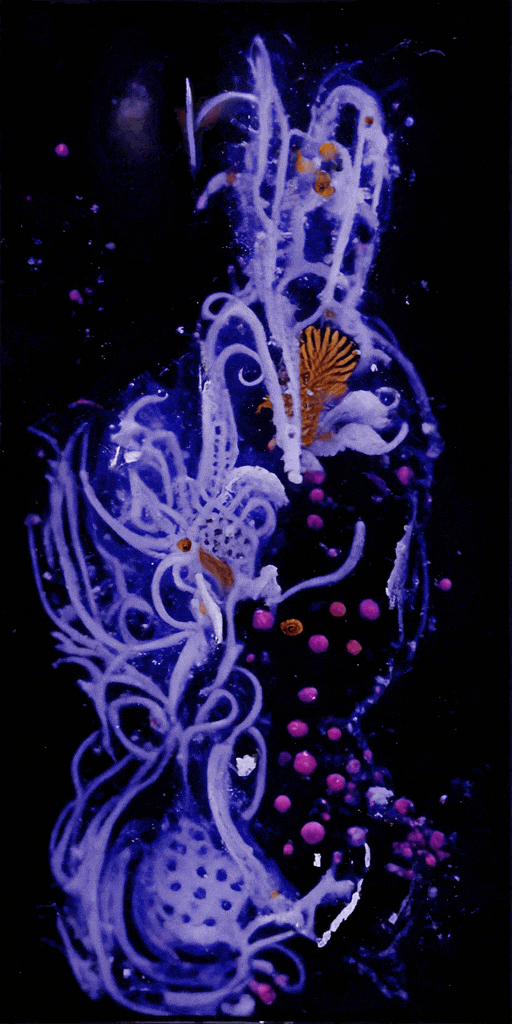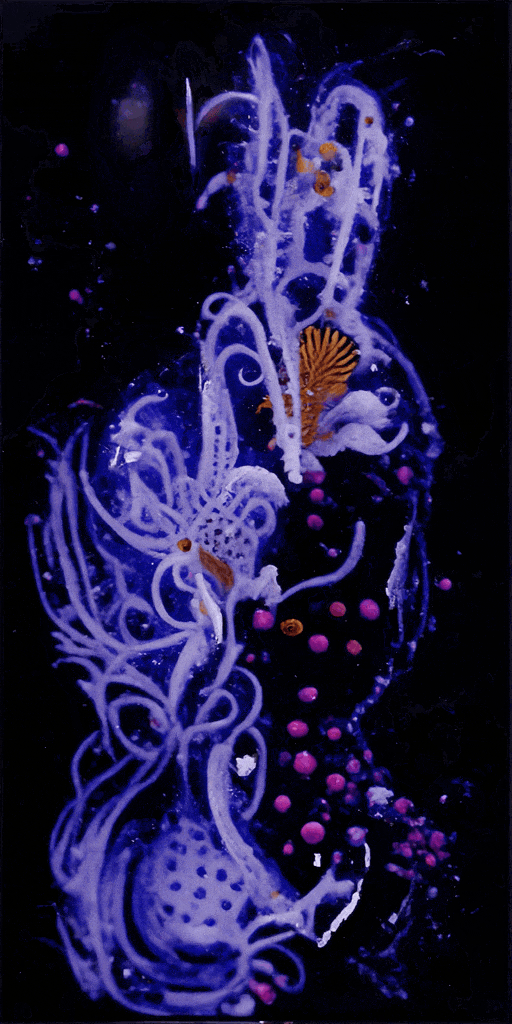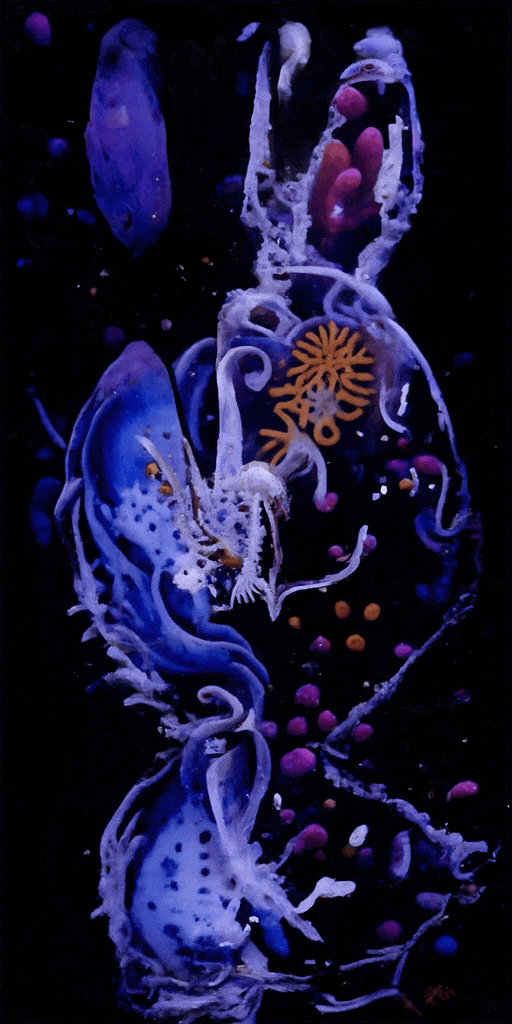
Sediment Nodes #1
Digital videos, custom generative adversarial networks (GANs), NFT, and Ethereum blockchain, 2022–23
Private collection
Entangled Others (Feileacan McCormick and Sofia Crespo) employs generative tools to portray the complex relationships, interactions, and interconnectedness between the human and nonhuman worlds. Their art uses a biologically informed model of computation (the neural network) to represent real and imagined species.
SedimentNodes was inspired by a real-life encounter with an underwater ecosystem. Crespo and McCormick, both avid divers, wanted to convey the experience of navigating sediment-laden waters after a storm. What at first appears to be a cloudy mass reveals a diverse ecosystem teeming with microscopic life-forms when illuminated. Sediment Nodes presents an evolving array of artificial organisms and landscapes, as if we’re discovering a vibrant world hidden just beneath the surface.
Crespo and McCormick’s creative process relies on custom-made generative adversarial networks (GANs) trained on images and video collected from their own dives, as well as custom synthetic data and publicly available imagery. These neural networks are modeled on the structure and functionality of brain neurons and can learn to detect patterns in source material to produce convincing fakes.
A subfield of artificial intelligence that uses generative models trained on large data sets to create new content—text, images, music, or videos—by mimicking the underlying structures, patterns, and styles of what it was trained on. Popular commercial generative AI tools like ChatGPT, Dall-E, and Midjourney use a chatbot feature where users can prompt the AI system using natural language rather than code. These large-scale systems are trained using trillions of data points collected from the internet and are controversial for the way they appropriate (and imitate) existing intellectual property and for their energy usage and environmental impact.
A type of learning algorithm associated with machine learning and artificial intelligence that is modeled and structured on how the human brain works. It uses interconnected nodes (like brain neurons) to process information, recognize patterns, and learn from data. By adjusting connections between nodes, it can improve at tasks like image recognition or language processing.
In object-oriented programming, a fundamental data structure that contains elements of the same type. Each element can be accessed using an index, which corresponds to its place within the array order. Indices start with 0 and ascend numerically. For example, the array areaCodes = [216, 419, 614] holds the area codes, in order, for Cleveland (index 0), Toledo (index 1), and Columbus (index 2), and these values are all integers. To return Toledo’s area code of 419, a programmer would run a command similar to: print(areaCodes[1]).
A type of machine learning system where two AI programs compete to improve each other. Both programs are trained on a dataset of text, images, or sound. One program (the generator) tries to create convincing artificial data, while the other (the discriminator) judges its authenticity. Through this contest, the generator learns to produce increasingly realistic outputs.

